What is an Off-Grid Solar System and How Much Does it Cost In 2024?
Harnessing the benefits of clean, green solar energy comes in various forms. One approach involves integrating solar power into the local electric grid to supplement existing energy sources, reduce utility bills, and establish a backup plan for blackouts. Alternatively, individuals can opt for a self-sufficient lifestyle by going entirely off-grid, generating power independently without relying on the conventional electricity grid, thus minimizing their carbon footprint.
However, it's crucial to recognize that transitioning to a fully off-grid lifestyle entails significant upfront costs. The investment required for an off-grid solar system may take time to recoup. The expense typically ranges from $5,000 to $30,000 for solar panels, depending on factors such as size, quantity, and quality.
Financial assistance through government programs and tax breaks can alleviate some of these costs over time, making renewable energy more accessible to a broader audience. In this article, we'll delve into the components of an off-grid solar power system and discuss factors influencing costs.
What is an Off-Grid Solar System?
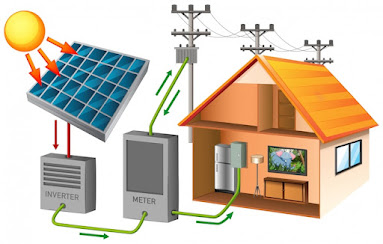
Components of an Off-Grid Solar Power System
Solar Panels:
Solar panels, equipped with photovoltaic solar cells, convert sunlight into energy. The number and size of panels depend on energy needs, with proper orientation to maximize sun exposure.
Solar Batteries:
Batteries store excess solar energy for use during periods of low sunlight or high demand. The battery bank ensures uninterrupted power supply, and costs typically range from $10,000 to $30,000 based on energy requirements.
Solar Inverter:
A solar inverter is essential for converting direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels into household-friendly alternating current (AC).
Charge Controller:
To prevent overcharging and ensure battery safety, a charge controller regulates the flow of electricity between solar panels and batteries. Different types, such as MPPT and PWM, offer varying efficiency levels.
Mounting and Wiring:
Proper installation involves mounting solar panels for optimal sunlight exposure and connecting all components to facilitate efficient energy transfer.
Factors Affecting System Costs
Several factors contribute to the wide range of prices associated with off-grid solar power systems:
System Size and Capacity:
The overall cost increases with the system's size and capacity, typically measured in kilowatts (kWh).
Quality and Efficiency of Components:
Higher-quality components, such as solar panels with greater efficiency, may have a higher upfront cost but can result in long-term savings.
Location and Installation Costs:
Geographical factors, such as sunlight availability, influence the number of solar panels needed. Installation costs, whether DIY or professional, also impact the total investment.
Maintenance and Upkeep:
While initial costs are significant, ongoing maintenance expenses are usually minimal, especially with durable components like lithium-ion or LFP batteries and long-lasting solar panels.
Estimating Costs and Choosing the Right System
To determine the appropriate off-grid solar power system, consider the following steps:
Estimate Energy Needs:
Evaluate your energy consumption by examining past bills. Use tools like the Power Kit Calculator to simplify the process and choose a system size that meets your requirements.
Consider Solar Panel Types:
Monocrystalline, thin-film, and polycrystalline panels vary in cost, efficiency, and lifespan. Assess your space constraints and budget to select the most suitable option.
Compare Brands and Parts:
Explore prices, customer reviews, and quality assessments for different components or entire systems to make informed decisions.
Explore Financing Options:
Investigate financing opportunities and government grants to ease initial financial burdens, making the transition to off-grid solar more affordable.
Get Quotes from Installers:
Obtain quotes from various solar installers to ensure competitive pricing and professional installation services.
Customize the System:
Tailor the off-grid solar system to your specific energy needs, keeping in mind potential future expansions.
Conclusion
Transitioning to an off-grid solar power setup requires careful consideration of costs, energy needs, and system components. By assessing these factors and leveraging available tools and resources, individuals can make informed decisions to achieve energy independence and long-term sustainability. Solar Earth Inc. offers Smart Solar Systems that provide a customizable and efficient solution for current and future energy requirements.

Comments
Post a Comment